- (t,m,s)-nets
- Low-discrepancy
- (t,s)-sequences
- Low-discrepancy
- 1-complex
- Homeomorphism:
- 1-neighborhood
- Neighborhoods
| Other
- 2-neighborhood
- Neighborhoods
- 3D triangles
- 3D to 3D
- acceleration vector
- 8.4.4.1
- acceleration-based control
- 8.4.4.1
| 8.4.4.1 to 8.4.4.1
- accelerometer
- Simple
- accessibility (of a roadmap)
- Roadmaps
- accessible system
- STLC:
| 15.4.3.5 to 15.4.3.5
- accumulation point
- Special
- Ackerman function
- 6.5.2
| 6.5.2
- action history
- 8.4.1.1
| History
- action sequence
- 14.2.2
- action trajectory
- 8.4.1.1
| 14.1.1
- active localization problem
- 12.2.1
- active-passive decomposition
- 7.4.2
| Active
- actuators
- Underactuation
- Adams methods
- Multistep
- adding integrators to a model
- 13.2.4 to 13.2.4.3
- adjoint transition equation
- 15.2.3
- adjoint variables
- 13.4.4
| 15.2.3
- admissible configurations
- Admissible
- affine space
- Varieties
- airport terminal
- Navigation
- algebraic primitive
- 3.1.2
| 3.1.2
| 3.1.2
| 3.1.2
| 3.1.2
| Some
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
- algebraic Riccati equation
- 15.2.2
- algebraic set
- 3.1.2
- alive states
- 2.2.1
| 2.3.3
| 2.3.3
| 8.5.2.3
- Allen wrench
- 12.5.2
- Alpha Puzzle
- A
| A
- alphabet
- 11.3.2
- Amato
- A
| A
- ambient isotopy
- Simplifying
- ambient space
- Simplifying
- analytic function
- Vector
- angular velocity
- Simple
| 13.1.2.2
| 13.1.2.2
| 13.1.2.3
| The
| The
| Differential
| Inertia
| The
| The
| A
| A
- annihilator
- 15.4.2.2
- antipodal points
- Higher
- approximate cell decomposition
- Further
- approximate cover
- 8.5.1.1 to 8.5.1.1
- approximate optimal motion planning
- General to General
- approximation algorithm
- Approximation
| Approximation to Approximation
- Ariadne's Clew algorithm
- Ariadne's to Ariadne's
- arrangement
- Further
- Asimo
- Virtual
| Virtual
- assembly planning
- Assembly to Assembly
- asteroids game
- 2D
- asymptotic convergence to a goal
- 8.4.1.1
- asymptotic solution plan
- 8.4.1.1
- asymptotic stability
- Asymptotic
| Asymptotic to Asymptotic
- atan2
- Determining
- automated farming
- 7.6
- automated guided vehicles
- Fixed-roadmap
- automotive assembly
- An
- autonomous differential equations
- Vector
- average cost-per-stage model
- 10.3
| Average
| Average to Average
- average dispersion
- Exercises
- averaging methods
- Averaging
| Averaging to Averaging
- axioms of rationality
- 9.5.1.2
| 9.5.1.2 to 9.5.1.2
- axis-aligned bounding box
- 5.3.2
| 5.3.2
- B-splines
- Nonuniform to Nonuniform
- backprojection
- 8.5.2.3
| Backprojections to Backprojections
| 14.5.2
| 14.5.2 to 14.5.2
| 14.6.3.4
- in preimage planning
- Backprojections to Computing
- backward action space
- Backward
- backward P. Hall coordinates
- The
| Returning
| Returning
| The
| The
| Using
- backward reachable set
- 14.2.1.3
| 14.2.1.3 to 14.2.1.3
- backward search
- Backward to Backward
| 5.4.1
| Computing
| Planning
| Computing
| Squeezing
- with backprojections
- Backward to Backward
- backward state transition equation
- Backward
| 2.3.1.2
| 2.3.2
- backward system simulator
- Reverse-time
- backward value iteration
- 2.3.1.1 to 2.3.1.1
- for reinforcement learning
- Value to Value
- for sequential games
- Value to Value
- on a nondeterministic I-space
- Value to Value
- on a probabilistic I-space
- Approximate to Exact
- path-constrained
- 14.6.3.4 to 14.6.3.4
- running time
- 2.3.1.1
- under differential constraints
- 14.5.2 to 14.5.2
- with average cost-per-stage
- Solutions to Solutions
- with discounted cost
- Value to Value
- with nature and continuous spaces
- 10.6.1 to 10.6.1
- with nondeterministic uncertainty
- Nondeterministic to Nondeterministic
| Convergence to Using
- with probabilistic uncertainty
- Probabilistic to Using
- bad bracket
- 15.4.3.5
- Balkcom-Mason curves
- 15.3.3
| 15.3.3 to 15.3.3
- Balkcom-Mason drive
- 15.3.3
- Balkcom-Mason metric
- 15.3.3
- bang-bang approach
- 14.6.3.5
| 14.6.3.5 to 14.6.3.5
- Barraquand-Latombe nonholonomic planner
- 14.4.2 to Backward
- base point (on a manifold)
- 15.4.2.2
- base point of a path
- The
- basis
- Vector
- of open sets
- Some
- Basu-Pollack-Roy roadmap algorithm
- 6.4.3
- Battle of the Sexes
- 9.4.1.1 to 9.4.1.1
- Battleship game
- 11.7.2 to 11.7.2
- Bayes' rule
- Conditional
| Marginalization
| A
| 11.2.3
| Discrete
- Bayesian classifier
- A
| A to A
- naive
- A
- behavioral strategies
- 11.7.1
- best-first search
- Best
| Best to Best
- bidirectional search
- Bidirectional to Bidirectional
| Further
| Expansive-space
| Exercises
| The
| 14.2.1.3
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| Backward
| Backward
| Tree-based
- balanced
- Balanced, to Balanced,
- for sampling-based planning
- 5.4.1
- bijective sensor
- 11.1.1
| 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- bilinear programming
- 9.4.1.2
- binding constraints
- 2.5.1
- bitangent line
- 6.2.4
- bitangent ray
- Critical
- bitmap
- Bitmaps to Bitmaps
- black-box simulators
- Black-box to Black-box
- Blum and Furst
- 2.5.2
- Blum and Kozen
- Algorithms
| Algorithms
- body density
- 13.3.3
- body frame
- Defining
| 4.4.3
| 4.4.3
| Drug
| Drug
| Exercises
| Important
| Simplifying
| Simplifying
| Completing
| The
- bond angle
- The
- bond length
- The
- Borel sets
- 5.1.3
| 5.1.3
- boundary grid point
- Discretization
- boundary of a set
- Special
- boundary point
- Special
- boundary representation
- 3.1
- boundary sensors
- Boundary to Boundary
- bounded set
- Homeomorphism:
- bounded-acceleration model
- 8.4.4.2
- bounded-velocity model
- 8.4.4.2
- Boustrophedon decomposition
- Boustrophedon to Spanning
- Brachistochrone curve
- 13.4.1.1
- bracket
- 15.4.3.1
- breadth-first search
- Breadth
- bridge-test sampling
- Bridge-test to Bridge-test
- broad-phase collision detection
- Two-phase
- Brockett
- 13.2.3
| 15.5.2
| 15.5.2.2
- Brockett's condition
- Time-varying
- bug algorithms
- 12.3.3
| 12.3.3 to Competitive
- bug trap
- 5.4.1
- Bug1 strategy
- The
| The to The
- Bug2 strategy
- The
| The to The
- caffeine
- Designing
| Designing
- calculus of variations
- 9.1.1.1
| 13.4.1.1
| 13.4.1.1 to 13.4.1.4
| Variational to Variational
- Campbell-Baker-Hausdorff-Dynkin formula
- The
- candidate Lyapunov function
- Determining
- Candorcet paradox
- 9.5.1.2
- Canny
- 6.4.3
- Canny's roadmap algorithm
- 6.4.3 to 6.4.3
| Further
| Combinatorial
| Fixed-path
| Combinatorial
- car pulling trailers
- Parking
| 13.1.2.4 to 13.1.2.4
- Caratheodory, solution sense of
- An
- card-counting strategies
- Exercises
- Carnot-Caratheodory metric
- The
- Cartesian product
- Cartesian
- carton folding
- Carton to Carton
- causal links
- 2.5.1
- CBHD formula
- The
- cell decomposition
- 6.2
| 6.3
| 6.3.1
| Simplicial to Complexity
| 12.2.2
| 12.4.3
- under differential constraints
- Decomposing to Decomposing
- center of mass
- 13.3.3
- Central Limit Theorem
- Generating
- chain of integrators
- 13.2.1.3
| 13.2.1.3 to 13.2.1.3
- chained-form system
- 15.4.3.2
| 15.5.2.3
| 15.5.2.3 to 15.5.2.3
- change of coordinates
- Coordinates
| Coordinates to Coordinates
- chasing a gap
- Critical
- Chazelle
- Warning:
- Chen-Fliess series
- The
| The to The
| Returning to Returning
- Chen-Fliess-Sussman equation
- The to The
- chi-square test
- Testing
- Chow-Rashevskii theorem
- 15.4.3.4
- Christoffel symbol
- 13.4.2
| 13.4.2
- Church-Turing thesis
- 1.4.1
- classification rule
- 9.2.4.1
- classifier
- 9.2.4.1
| 9.2.4.1 to A
- cleared region
- 12.4.2
- closed kinematic chains
- What
| 4.4 to 4.4.3
- motion planning for
- 7.4 to Computing
- closed set
- Closed
- closed system (in mechanics)
- Closed to Closed
- closed-loop
- control law
- Open-loop
- plan
- 8.1
- closure of a set
- Special
| Denseness
- closure space
- Closure
- codistribution
- 15.4.2.2
- coherent models
- 5.3.3
- collision detection
- 5.3 to 5.3.4
- broad-phase
- Two-phase
- checking a path segment
- 5.3.4 to 5.3.4
- hierarchical methods
- 5.3.2 to 5.3.2
- incremental methods
- 5.3.3 to 5.3.3
- narrow-phase
- Two-phase
- two-phase
- Two-phase to Two-phase
- collision pairs
- Obstacle
- collision-detection
- 14.3.1.3 to 14.3.1.3
- collocation
- 14.7
- combinatorial motion planning
- 6. to Specialized
- cell decompositions
- 6.3 to Complexity
- introductory concepts
- 6.1 to Roadmaps
- polygonal case
- 6.2 to 6.2.4
- combinatorial roadmaps
- 5.6
- commutative group
- Groups
| 15.4.2.3
- commutative ring
- Polynomials
- commutator
- 15.4.2.3
- commutator motion
- 15.4.2.3 to 15.4.2.3
| 15.5.1
- compass
- Simple
| 12.2.2
- compatible coordinate neighborhoods
- Coordinates
- competitive ratio
- Landmark
| Competitive
| Competitive to Competitive
- complementary pair
- 2.4.1
- complete exclusion axiom
- 2.5.3
- completely integrable
- 13.1.3.4
| 15.4.2.1
| 15.4.2.1 to 15.4.2.1
- completeness
- overview
- Notions to Notions
- complex
- 6.3.1
| 6.3.1
| 6.3.1 to Singular
- complexity class
- Languages
- complexity of motion planning
- 6.5 to Specialized
- lower bounds
- 6.5.1 to Lower
- upper bounds
- 6.5.3 to Specialized
- compliant motions
- 12.5.1
| Compliant
| Compliant to Compliant
| Backprojections
- composition of funnels
- 8.5.1 to Termination
| Squeezing
| Domains
- compressed mode
- 7.3.1
- computational algebraic geometry
- 6.4 to 6.4.3
- Conchoid of Nicomedes
- Critical
| Exercises
- conditional Bayes' risk
- Optimal
- conditional Bayes' rule
- Conditional
- conditional expectation
- Expectation
- conditional independence
- Conditional
- conditional probability
- Conditional
| Conditional to Conditional
- configuration space
- 4.
| 4.
| 4.2 to 4.4.3
- of 2D rigid bodies
- 4.2.1 to Interpreting
- of 3D rigid bodies
- 4.2.2 to Special
- of chains of bodies
- 4.2.3 to 4.2.3
- of trees of bodies
- 4.2.3 to 4.2.3
- velocity constraints on
- 13.1 to 13.1.3.4
- conformations
- The
| Drug
- connected space
- Connected
- connectivity-preserving roadmap
- Roadmaps
- connector in a roadmap
- 5.6.2
- conservative approximations
- 11.4.3.2
| Conservative to Conservative
- conservative system
- 13.4.1.2
- constant vector field
- Vector
- constant-sum game
- Exercises
- contaminated region
- 12.4.2
- continuous Dijkstra paradigm
- Euclidean
- continuous function
- Continuous
- continuous-steering car
- 13.2.4.2
| 13.2.4.2 to 13.2.4.2
- contractible space
- The
- control system
- 13.
| Open-loop
- control-affine system
- 13.2.3
| 15.4.1 to 15.4.1
- controllability matrix
- Classical
- controllability of a system
- 15.1.3 to STLC:
- linear case
- Classical to Classical
- controlled Markov process
- 10.1.1
- convex hull
- 5.3.2
| 5.3.2
| Piecewise-smooth
- convex polygon
- Convex to Convex
- convex set
- Convex
- convolution
- 4.3.2
- cooperative game theory
- Further
- coordinate neighborhood
- Coordinates
- coordinates
- Coordinates
- coordination space
- Fixed-path
| Fixed-path
- Coriolis matrix
- 13.4.2
- cost functional
- 2.3
| General
| 7.7.2
| 10.1.1
| Discounted
| 11.7.2
| 14.5.2
- approximating
- Approximating
- quadratic
- 15.2.2
- cost-to-come
- Dijkstra's
| 2.3.1.2
| 2.3.1.2 to 2.3.1.2
| 14.2.1.2
- cost-to-go
- A-star
| 2.3.1.1 to 2.3.1.1
| General
| Feasibility
| Navigation
| Navigation
| Computing
| Wavefront
| Dial's
| 8.4.1.2
| 8.4.3
| 8.4.3
| 8.4.3
| 8.4.3
| 8.4.3
| 8.5.1
| 8.5.2.1
| 8.5.2.1
| Continuous
| 8.5.2.2
| Obtaining
| Handling
| Using
| 8.5.2.3
| 8.5.2.3
| 8.5.2.3
| 8.5.2.3
| 8.5.2.3
| 10.6.1
| The
| The
| Distance
| Distance
| 14.5.2
| 14.5.2
| 14.5.2
| 14.5.2
| 14.5.2
| 14.5.2
| 14.6.3.4
| 14.6.3.4
- Coulomb friction
- Compliant
- counting measure
- 5.1.3
| 5.1.3 to 5.1.3
- covariance matrix
- Moment-based
- cover of a set
- 8.5.1.1
- approximate
- 8.5.1.1
- coverage planning
- 7.6
| 7.6 to Spanning
- Coxeter-Freudenthal-Kuhn triangulation
- 8.5.2.1
- critical curves
- Critical
- critical gap events
- Critical to Critical
- critical point of a function
- 6.4.3
| 8.4.4.3
- cube complex
- Cube
| Cube
| Cube to Planning
- cubical partition
- Decomposing
- CW-complex
- 6.3.1
- cycloid function
- 13.4.1.1
- cylinder over a cell
- Cylindrical
| Critical
| The
- cylindrical algebraic decomposition
- 6.4.2 to Solving
| Combinatorial
| Fixed-path
- for motion planning
- Solving to Solving
- cylindrical decomposition
- Cylindrical
| Cylindrical to Cylindrical
- D'Alembert
- 13.4.3.1
- Davenport-Schinzel sequence
- 6.5.2
| 6.5.2 to 6.5.2
- Davis-Putnam procedure
- 2.5.3
- dead states
- 2.2.1
| 2.2.1
| Dijkstra's
| Dijkstra's
| 8.5.2.3
- decision maker
- 1.1
| 9.
- decision problem
- The
| The to The
- decision theory
- 9.
- decision vertex (in a game tree)
- 10.5.1
- decoupled planning
- Reasons
| 14.6 to 14.6.3.5
- decoupling vector fields
- 14.6.3.2
| Decoupling
| Decoupling to Decoupling
- deformation retract
- 6.2.3
- degrees of freedom
- Translation
- delayed-observation sensor
- 11.1.1
| 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- Denavit-Hartenberg parameters
- 3.3.2
| 3.3.2 to Two
| The
| The
| 4.2.2
| 4.2.3
| Chains
| 4.4.3
- dense sequence
- Denseness
| 14.2
- dense set
- Denseness
| Denseness
| Denseness
- dependent events
- Conditional
- depth-first search
- Depth
| Depth to Depth
- depth-mapping sensors
- Depth-mapping to Depth-mapping
- derivation (on a manifold)
- Tangent
- derived information space
- 11.2
| 11.2.1 to Sensor
| 11.4.3 to 11.4.3.3
- for continuous time
- 11.4.3.3 to 11.4.3.3
- derived information transition equation
- Constructing
- determining the environment
- 12.3.1 to 12.3.1
| 12.3.1
| Algorithms to Algorithms
- deterministic finite automaton
- 2.1.2
| 11.3.2
- language
- 2.1.2
- deterministic plan
- 10.5.1
| Defining
| 11.7.1
- Dial's algorithm
- Dial's to Dial's
| Other
- diameter function
- Squeezing
- dielectric constant
- Drug
- diffeomorphic spaces
- Smoothness
- diffeomorphism
- Smoothness
- differential drive
- 15.4.3.4
- model
- 13.1.2.2 to 13.1.2.2
- second-order
- 13.2.4.3
- showing it is nonholonomic
- 15.4.2.4 to 15.4.2.4
- differential game
- 13.5.2
| 13.5.2
| 13.5.2 to 13.5.2
- against nature
- 13.5.1
- pursuit-evasion
- 13.5.2
- differential inclusion
- Piecewise-smooth
| 13.5.1
- differential models
- 13. to 13.5.2
- conversion from implicit to parametric
- 13.1.1.3 to 13.1.1.3
- implicit representation
- 13.1.1.1 to General
- parametric representation
- 13.1.1.2 to 13.1.1.2
- differential rotations
- Differential to Differential
- differentially flat systems
- Differentially to Differentially
- digital actor
- Virtual
| Virtual
| Virtual
- Dijkstra's algorithm
- 2.
| Dijkstra's to Dijkstra's
| 2.3.3 to 2.3.3
| Computing
| Computing
| Wavefront
| Wavefront
| Wavefront
| Dial's
| 8.4.2
| 8.4.3
| 8.4.3
| 8.5.2.3
| 8.5.2.3
| 8.5.2.3
| 8.5.2.3
| 10.6.1
| 12.3.2
| 12.3.2
| 12.3.2
| 14.4.1.1
| 14.5.2
| 14.5.2
| 14.6.3.4
- extension of to continuous spaces
- 8.5.2.3 to 8.5.2.3
- with nondeterministic uncertainty
- Nondeterministic to Nondeterministic
- with probabilistic uncertainty
- Probabilistic to Probabilistic
- dimension
- of a manifold
- Manifold
- of a vector space
- Vector
- directed roadmap
- Sampling-based
- Dirichlet boundary condition
- 8.4.4.4
- disconnection proof
- Further
- discount factor
- Discounted
- discounted cost model
- 10.3
| Discounted
| Discounted to Discounted
- discrepancy
- 5.2.4 to Low-discrepancy
| 14.3.1.2 to 14.3.1.2
- range space
- 5.2.4
- relation to dispersion
- Relating
- discrete feasible planning
- 2.1.1
- discrete-time model
- 14.2.2
| 14.2.2 to 14.2.2.3
- dispersion
- 5.2.3
| Dispersion to Dispersion
| 8.5.2.1
| 14.3.1.2 to 14.3.1.2
- relation to discrepancy
- Relating
- distance between sets
- Distance to Distance
- distance function
- Distance
- distribution (of vector fields)
- 15.4.2.2 to 15.4.2.2
- regular
- 15.4.2.2
- singular
- 15.4.2.2 to 15.4.2.2
| 15.4.2.2
- disturbed odd/even sensor
- 11.1.1
- disturbed sign sensor
- 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- domain of attraction
- Domains
| Domains to Domains
- dominated action
- 9.1.1.2
- dominated plan
- 7.7.2
- Donald
- Further
| Backprojections
- double integrator
- 13.2.1.1
| 13.2.1.1 to 13.2.1.1
| 13.2.4.3
| 13.3.2.1
| The
| 14.1.1
| Kinodynamic
| 14.1.3.2
- lattice
- 14.4.1 to Underactuated
- optimal planning for
- 15.2.3 to 15.2.3
- doubly connected edge list
- Polyhedral
| 6.2.1
| 6.2.1
| Algorithm
| Algorithm
| Algorithm
- drift
- 13.2.1.3
| 13.2.3
| Drift
| 15.4.1
- driftless
- 13.2.3
| Drift
- driftless system
- 13.2.1.3
| 15.4.1
- controllability
- 15.4.3.4 to 15.4.3.4
- drug design
- Designing
| Drug to Drug
- Dubins car
- 13.1.2.1
| 13.5.2
| Symmetric
| 14.1.3.2
| 14.2.1.2
| 14.2.1.2
| 14.2.1.2
| 14.2.1.2
| 14.2.2.1
| 14.2.2.1
| 14.2.2.3
| The
| 14.3.3
| 14.4.2
| Searching
| Searching
| Resolution
| Resolution
| Resolution
| Distance
| 14.5.1
| 14.6.1
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.3.2
- plan-and-transform approach
- 14.6.2 to 14.6.2
- reachability tree of
- 14.2.2.1 to 14.2.2.1
- Dubins curves
- 15.3.1
| 15.3.1 to 15.3.1
- Dubins metric
- 15.3.1
- dynamic constraints
- 15.4.1
- dynamic programming
- 2.
- applied to steering
- Dynamic to Dynamic
- continuous-time
- 15.2 to Time
- dynamics
- of a particle
- 13.3.2 to 13.3.2.1
- of a rigid body
- 13.3.3 to A
- of a set of particles
- 13.3.2.2 to 13.3.2.2
- of a two-link manipulator
- 13.4.2.1 to 13.4.2.1
- of chains of bodies
- 13.4.2 to 13.4.2.1
- of constrained bodies
- 13.4.3.1 to 13.4.3.1
- with nonconservative forces
- 13.4.3.2 to 13.4.3.2
- efficient algorithm
- Languages
| Lower
| General
- elongated mode
- 7.3.1
- EM algorithm
- The to The
- embedding of a manifold
- Manifold
- energy function
- 7.5
| Simplifying
| Drug
- equilibrium point of a vector field
- Equilibrium
- Erdmann
- Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
- error detection and recovery (EDR)
- Backprojections
- Euclidean metric
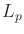
- Euclidean motion model
- General to General
- Euclidean norm
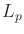
- Euclidean shortest paths
- Euclidean to Euclidean
- Euler angles
- Further
- Euler approximation
- Obtaining
- Euler-Lagrange equation
- 13.4.1.1
| 13.4.1.1
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.3
| 13.4.1.4
| 13.4.1.4
| 13.4.2
| 13.4.2
| 15.2.3
| 15.4.1
| 15.5.2.1
| Pontryagin's
| Pontryagin's
| Pontryagin's
- with conservative forces
- 13.4.3.2
- event space
- Probability
- exit face
- 8.4.2
- expansive-space planner
- Expansive-space to Expansive-space
- expectation of a random variable
- Expectation to Expectation
- expected-case analysis
- 9.2.2
| The
| The
- exploration vs. exploitation
- The
- exponential map
- The to The
- exponentially stable system
- Asymptotic
- EXPTIME
- Languages
- extended Kalman filter
- 11.6.1
| Continuous
- extended system
- 15.5.1
- exterior point
- Special
- extremal function
- 13.4.1.1
- falling particle
- 13.4.1.2 to 13.4.1.2
- fast Fourier transforms
- Handling
- Faure sequence
- Low-discrepancy
- feasible planning
- discrete
- 2.1.1
- with feedback
- Feasibility to Feasibility
- feasible space (for closure constraints)
- Closure
- feature space
- 9.2.4.1
- feature vector
- 9.2.4.1
| A
| A
| A
- feedback motion planning
- complete, optimal
- 8.4.3 to 8.4.3
- complete, some dynamics
- 8.4.4 to 8.4.4.4
- definitions
- 8.4.1 to 8.4.1.2
- motivation
- 8.1 to 8.1
- sampling-based
- 8.5 to 8.5.2.3
- under differential constraints
- 14.5 to 14.5.2
- feedback plan
- 8.2.1
| 8.2.1 to 8.2.1
| Defining
| Defining to The
- cost of
- The to The
- graph representation of
- Graph to Graph
- information feedback
- 11.1.3 to 11.1.3
- over a cover
- 8.5.1.2 to 8.5.1.2
- sensor feedback
- Sensor
- feedback planning
- discrete
- 8.2 to Other
- feedback stabilization
- 15.1.1
- fiber over a base
- 15.4.2.2
- fictitious action variable
- 15.5.1
- field
- Fields
| Fields
| Fields to Fields
- algebraically closed
- Real
- Filipov, solution sense of
- Piecewise-smooth
| Vector
- finite state machine
- 2.1.2
- firetruck
- 13.1.2.4
- first-order controllable systems
- 15.5.2.2
| 15.5.2.2 to 15.5.2.2
- first-order theory of the reals
- The
- fixed point of a vector field
- Equilibrium
- fixed-path coordination
- Fixed-path to Fixed-path
- fixed-roadmap coordination
- Fixed-roadmap to Planning
- flashlight example
- 2.4.1 to 2.4.1
- Boolean expression for
- 2.5.3
- planning graph of
- Mutex
- flashlight sensor
- 12.4.3
- flat cylinder
- 2D
- flat outputs
- Differentially
| Differentially
- flat torus
- 2D
- flexible materials
- Flexible
- flying an airplane
- 13.1.3.2 to 13.1.3.2
- folding problems
- 7.5 to Protein
- foliation
- 14.2.1.1
| 15.4.2.1
- force
- Newton's
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.2
| 13.3.3
| 13.3.3
| 13.3.3
| The
| The
| A
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
- resultant
- 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.2
- force sensor
- Boundary
- formal Lie algebra
- Formal to The
- forward projection
- 10.1.2
| 14.2.1.2
- differential
- 13.5.1 to 13.5.1
- nondeterministic
- Nondeterministic to Nondeterministic
- probabilistic
- Probabilistic to Probabilistic
- under a fixed plan
- Forward to Forward
- forward search
- 2.2.1 to Iterative
- A
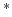 algorithm
algorithm
- A-star
- A
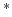 algorithm
algorithm
- to A-star
- best first
- Best to Best
- breadth-first
- Breadth to Breadth
- depth-first
- Depth to Depth
- Dijkstra's algorithm
- Dijkstra's to Dijkstra's
- general, discrete
- 2.2.1 to 2.2.1
- iterative deepening
- Iterative to Iterative
- forward value iteration
- 2.3.1.2 to 2.3.1.2
- four-bar mechanism
- Three
- frame axiom
- 2.5.3
- Fraunhofer Chalmers Centre
- Sealing
| Sealing
- Frazzoli
- 14.2.3
| 14.2.3
- free space
- Obstacle
- free variables
- Tarski
- frequentist
- 9.5.2.1 to 9.5.2.1
- frequentist risk
- 9.5.2.1
- friction cone
- Compliant
- Frobenius theorem
- 15.4.2.4 to 15.4.2.4
- frontier set
- 8.5.2.3
| Nondeterministic
| 14.5.2
- fully actuated system
- Underactuation
- function space
- Vector
| 11.4.1
| 13.4.1.1
- functional
- 13.4.1.1
| 13.4.1.1
- shortest-path
- 13.4.1.1
- fundamental group
- The
| The to The
- higher order
- The
- of a simply connected space
- The to The
- of
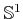
- The
- of
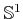
- to The
- of
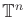
- The
- of
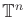
- to The
- of
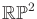
- The
- of
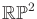
- to The
- Fundamental Lemma of the Calculus of Variations
- 13.4.1.1
- Gabriely and Rimon
- Spanning
- gain constant
- 8.4.4.1
- game
- alternating-play model
- 10.5.1
| 11.7.1
- extensive form
- 10.5.1
- ladder-nested
- 11.7.1
- normal form
- 10.5.1
- open-loop model
- 10.5.1
| 11.7.1
- stage-by-stage model
- 10.5.1
| 11.7.1
- unusual information model
- 11.7.1 to 11.7.1
- game against nature
- 9.2 to 9.2.4.2
- sequential
- 10.1 to The
| 10.6.1 to 10.6.2
- game graph
- 10.5.2
- game theory
- 9.
| 9.
| 9.3
| 9.3 to 9.4.2
| 9.5.4 to 9.5.4
| 10.5 to Introducing
| 11.7 to 11.7.2
- information spaces in
- 11.7 to 11.7.2
- game tree
- 10.5.1
| 10.5.1
| 10.5.1 to 10.5.1.3
- information space over
- 11.7.1 to 11.7.1
- gap navigation tree
- 12.3.4 to I-space
- gap sensor
- Depth-mapping
- gap theorems
- Real
- garage configuration
- Fixed-roadmap
- Gaussian sampling
- Gaussian to Gaussian
- Geiger counter sensor
- Landmark
- general linear group
- Matrix
- general position
- General
| General to General
| Critical
- generalized coordinates
- 13.4.1.2
- generalized cylinder
- Generalized
- generalized damper model
- Compliant
- generalized forces
- 13.4.1.3
| 13.4.1.4
| 13.4.1.4
| 13.4.3.1
- generalized momentum
- 13.4.4
- generator of a lattice
- Making
- geodesics
- 13.4.1.2
| Riemannian
- geometric modeling
- 3.1 to Generalized
- Gilbert-Johnson-Keerthi algorithm
- Further
- gingerbread face
- 3.1.2
| Semi-algebraic
| The
- globally asymptotically stable
- Domains
- globally positive definite
- Determining
- globally randomized plan
- 11.7.1
- goal recognizability
- 11.3.1 to 11.3.1
| Backprojections
- goal sensor
- 12.3.3
- Goldberg and Mason
- Squeezing
- golden ratio
- Low-discrepancy
- Goursat normal form
- 15.5.2.3
- Grübler's formula
- 4.4.3
- gradient descent
- Navigation
| 8.4.1.2
| 8.4.4.3
- graph search
- on an information space
- Graph-search to The
- grasped configurations
- Stable
- gray-scale map
- Bitmaps
| 12.3.2
- great circle
- 5.1.2
- grid
- 7.1.3
- 2D planning on
- 2.1.2
- feedback plan on
- Feasibility to Feasibility
- infinite sequence
- Infinite to Infinite
- multi-resolution
- Infinite
- navigation function on
- Navigation to Navigation
| 8.2.3 to Other
- neighborhoods
- Neighborhoods to Neighborhoods
- partial
- Infinite
- resolution issues
- Grid to Grid
- set of environments
- 12.3.1 to Algorithms
- grid point
- Discretization
- grid resolution
- 5.2.3
- group
- Groups
- group axioms
- Groups
| Groups to Groups
- guaranteed reachable
- Convergence
- guard in a roadmap
- 5.6.2
- gyroscope
- Simple
- Haar measure
- 5.1.4
| 5.1.4 to 5.1.4
- hairy ball theorem
- 8.4.1.1
- half-edge
- Polyhedral
| 6.2.1
- half-plane
- Convex
- half-space
- Polyhedral
- Halton sequence
- Low-discrepancy
| Low-discrepancy to Low-discrepancy
- Hamilton's equations
- 13.4.4
| 15.2.3
| 15.4.1
| Pontryagin's
| Pontryagin's
- Hamilton's principle of least action
- 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2 to 13.4.1.2
- Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equation
- 10.2.2
| 15.2.1
| 15.2.1.2 to 15.2.1.3
- Hamilton-Jacobi-Isaacs equation
- 15.2.1.3
- Hamiltonian function
- 13.4.4
| 13.4.4
| 15.2.3
| 15.2.3
- Hammersley point set
- Low-discrepancy
| Low-discrepancy to Low-discrepancy
- harmonic potential function
- 8.4.4.4 to 8.4.4.4
- Hausdorff axiom
- Some
- Hausdorff space
- Some
- helicopter flight
- 14.2.3
- Hessian
- 8.4.4.3
- hide and seek
- Playing
- hierarchical inclusion of a plan
- Hierarchical
| 12.5.1
- hierarchical planning
- Hierarchical
| Manipulation
- higher order controllability
- 15.5.2.3
- Hilbert space
- Vector
- hill function
- Determining
- history
- History
| History to History
- history information space
- 11.1.2
| The to The
| 11.4.2 to 11.4.2
- at stage
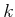
- The
- at time
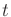
- 11.4.2
- history information state
- History
| History to History
- history-based sensor mapping
- 11.4.1
| 11.4.2
- hitch length
- 13.1.2.4
- holonomic
- 13.1.3.4
| 15.4.2.1
- homeomorphic spaces
- Homeomorphism:
- homeomorphism
- Homeomorphism:
| Homeomorphism: to Homeomorphism:
| Smoothness
| Coordinates
- homicidal chauffeur
- 13.5.2
| 13.5.2 to 13.5.2
- homing sensor
- Landmark
- homogeneous transformation matrix
- Combining
| Combining
| no title
| Homogeneous
| Homogeneous
| 3.3.2
| Two
| no title
| The
| The
| The
| The
| The
| Linear
| Exercises
| 4.2.1
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| Chains
- homology
- The
- homotopic paths
- Simply
- humanoid
- Virtual
| Virtual
| Virtual
| Virtual
| Virtual
| Junctions
- hybrid state space
- 7.3.1
| 7.3.1
- hybrid system
- 7.3
| 7.3.1 to 7.3.1
| Piecewise-smooth
| Piecewise-smooth
- motion planning
- 7.3.1
- with nature
- 10.6.2 to 10.6.2
- ibuprofen
- Designing
| Designing
- ideal distance function
- The to The
- identification of points
- Identifications
- identity sensor
- 11.1.1
| Linear
- implicit function theorem
- 13.1.1.3
- implicit velocity constraints
- General
- improper prior
- 9.5.2.2
- incomparable actions
- 9.1.1.2
- incremental distance computation
- 5.3.3
- incremental sampling and searching
- adapting search algorithms
- 5.4.2 to Grid
- general framework
- 5.4.1 to 5.4.1
- under differential constraints
- 14.4 to Sampling-based
- independent events
- Conditional
- independent-joint motion model
- General to General
- inertia matrix
- Inertia
| Inertia
| Inertia to Simplifying
| 13.4.1.2
- inertial coordinate frame
- Inertial
| Inertial to Inertial
| Newton's
| Important
| The
| The
| The
| The
| 13.4
| 13.4.1.2
- infimum
- 9.1.1.1
- infinite reflection (in a game)
- 9.5.4
- infinite-horizon problem
- 10.3
| 10.3 to Solutions
- inflection ray
- Critical
- information mapping
- 11.2.1
| 11.2.1 to Constructing
- sufficient
- Constructing to Constructing
- information space
- 11. to 11.7.2
- continuous examples
- 11.5 to 11.5.4
- continuous time
- 11.4.2 to 11.4.2
- conversion to a state space
- The to The
| 12.1.1 to 12.1.1
- discrete examples
- 11.3 to 11.3.3
- for game theory
- 11.7 to 11.7.2
- in continuous state spaces
- 11.4 to 11.5.4
- limited memory
- 11.2.4 to Sensor
- sensor feedback
- Sensor to Sensor
- information state
- 11.
| 11.
- information transition equation
- The to The
- derived
- Constructing to Constructing
- information transition function
- The
- information-conservative property
- 12.4.2
- information-feedback plan
- 11.1.3
- initial condition space
- The
| The to The
| 11.4.1 to 11.4.1
- input string
- 11.3.2
- integrable system
- 13.1.3.4
- integral curve
- An
| An to An
- integral manifold
- 15.4.2.1
- interior of a set
- Special
- interior point
- Special
- interpolation neighbors
- 8.5.2.1
- interpolation region (for value iteration)
- 8.5.2.1
| 10.6.1
- interval homeomorphisms
- Homeomorphism: to Homeomorphism:
- intractable problem
- Languages
- inverse Ackerman function
- 6.5.2
- inverse control problem
- Reverse-time
- inverse kinematics problem
- What
- involutive distribution
- 15.4.2.4
- Isaacs
- 13.5.2
| 13.5.2
- isomorphic graphs
- Homeomorphism:
- isomorphic groups
- Using
- isomorphism
- Homeomorphism:
- iterative deepening
- Iterative
| Iterative to Iterative
- Jacobi identity
- 15.4.3.1
| 15.4.3.3
| 15.4.3.3
| 15.5.2.2
- Jacobian
- 6.4.3
- jerk (third time derivative)
- 13.2.1.3
| 14.6.3.4
- joint encoder
- Simple
- junction of links
- Junctions
- Kagami
- Virtual
| Virtual
- Kalman filter
- 11.6.1 to 11.6.1
- Kalman rank condition
- Classical
- Kd-tree
- Approximate
| Approximate to Approximate
| Defining
| Maintaining
- Khalil-Kleinfinger parameterization
- Junctions
- Khatib
- 8.4.1.2
- kidnapped-robot problem
- 12.2
- kinematic chain
- 3.3
- kinematic constraints
- Nonholonomic
| 15.4.1
- kinematic singularities
- Computing
- kinematically controllable
- Decoupling
- kinematics for wheeled systems
- 13.1.2 to 13.1.2.4
- Kineo CAM
- An
| An
| An
| Parking
| Parking
- kinetic energy
- 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| Completing
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.4
| 13.4.1.4
| 13.4.2
| 13.4.2.1
| 13.4.2.1
| 13.4.3.1
- kinodynamic planning
- Kinodynamic
| Kinodynamic to Kinodynamic
| 14.4.1 to Underactuated
- Klein bottle
- 2D
- knot
- Simplifying
- knot simplification
- Simplifying to Simplifying
- knot vector
- Nonuniform
- Koditschek
- Navigation
| 8.4.4.3
- Kolmogorov complexity
- 2.4.1
| Lower
- Kuffner
- A
| A
| 5.4.1
- Kuhn
- 11.7.1
| Further
- Kutzbach criterion
- 4.4.3
- L-shaped corridor example
- 11.3.1 to 11.3.1
- label-correcting algorithms
- 2.3.3
| 2.3.3 to 2.3.3
- Lafferriere and Sussmann
- 15.5.1
- Lagrange multiplier
- 13.4.3.1
- Lagrangian function
- 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.4
| 13.4.2.1
| 13.4.3.1
| 13.4.4
- Lagrangian mechanics
- 4.
- landmark region detector
- Landmark
- landmark sensors
- Landmark to Landmark
- language
- 2.1.2
| 11.3.2
- latitude in a grid
- Algorithms
- Latombe
- 4.
- lattice
- Making
| Making
| Making
| Low-discrepancy
- for unconstrained mechanical systems
- Unconstrained to Unconstrained
- Laumond
- Parking
| Parking
| Nonholonomic
- lawn mowing
- 7.6
- layered graph
- Planning
- layered plan
- Plan
- learning phase
- The
- leaves of a foliation
- 14.2.1.1
| 15.4.2.1
- Lebesgue integral
- 5.1.3
- Lebesgue measure
- 5.1.3
| 5.1.3 to 5.1.3
- left translation
- 15.4.3.1
- left-invariant vector field
- 15.4.3.1
- left-turn predicate
- 6.2.4
- Legendre transformation
- 13.4.4
- Legendre-Clebsch condition
- 15.2.3
- Leibniz rule
- Tangent
- Lennard-Jones radii
- Drug
- Lens spaces
- Higher
- level-set method
- Further
- Lie
- 15.4.2
- Lie algebra
- 15.4.3.1
| 15.4.3.1
| 15.4.3.1 to 15.4.3.2
- cross product example
- 15.4.3.1 to 15.4.3.1
- of the system distribution
- 15.4.3.2 to 15.4.3.2
- on Lie groups
- 15.4.3.1 to 15.4.3.1
- Lie algebra rank condition
- 15.4.3.4
- Lie bracket
- 15.4.2.3
| 15.4.2.3 to 15.4.2.3
| 15.4.3.1
- Taylor series approximation of
- 15.4.2.3 to 15.4.2.3
- Lie derivative
- Determining
- Lie group
- Matrix
| 15.4.3.1
| 15.4.3.1
- ligand
- Drug
- limit curve
- 14.6.3.5
- limit cycle
- Limit
| Limit to Limit
- limit point of a set
- Special
- Lin-Canny
- Further
- line-segment robot
- 6.3.4 to Complexity
- linear combination
- Vector
- linear complementarity problem
- 9.4.1.2
- linear differential game
- 13.5.2
| 13.5.2
- linear interpolation
- 8.5.2.1
- linear momentum
- 13.3.2.1
- linear programming
- 9.1.1.1
| 9.3.3.2
| 14.7
- linear sensing models
- Linear
| Linear to Linear
- linear space
- Vector
- linear system
- 13.2.2
| 13.2.2 to 13.2.2
- observability
- 13.2.2
- time-varying
- 13.2.2
- linear transformations
- Linear
- linear-Gaussian system
- 11.6.1
| 11.6.1
| Continuous
- linear-quadratic problems
- 15.2.2 to 15.2.2
- linear-quadratic-Gaussian (LQG) system
- 11.6.1
| 15.2.2
- link
- 3.3
- linkage
- 3.3
- linkage graph
- 4.4.3
- Lipschitz condition
- 5.3.4
| An
| An to An
| 14.2.2.3
| 14.2.2.3
| 14.2.2.3
| 14.3.4
| Resolution
| 14.5.2
| 14.7
- Lipschitz constant
- 5.3.4
| An
- LMT framework
- 12.5.1
- local operator
- Navigation
| Navigation
| Navigation to Navigation
| Computing
| 8.2.3
| 8.4.1.2 to 8.4.1.2
| 8.4.2
| 8.4.4.3
| Using
| 14.5.2
- continuous space
- 8.4.1.2
- local planning method
- 5.4.1
| 5.4.1
| 5.4.1
| 5.4.1
| 5.4.1
| 5.4.3
| 5.4.3
| Ariadne's
| Expansive-space
| Random-walk
| 5.5.1
| Generic
| Some
| Some
| Some
| Planning
| 14.7
| 15.
| STLC:
| 15.3
| 15.3.1
| 15.3.1
| 15.3.2
| 15.3.3
| 15.4.3.4
| 15.5
| Decoupling
- in plan-and-transform
- 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
| 14.6.2
- under differential constraints
- 14.3.3
| 14.3.3 to 14.3.3
| 14.3.4
| 14.4.3
| 14.4.3
| 14.4.3
| Designing
| Designing
- local visibility sensor
- 12.3.3
- localization
- 12.2 to The
- active
- 12.2
| Solving to Solving
- combinatorial
- 12.2.2 to 12.2.2
- discrete
- 12.2.1 to Other
- passive
- 12.2
| 12.2.1
| Solving to Solving
- probabilistic
- 12.2.3 to Continuous
- symmetries
- Solving to Solving
- locally positive definite
- Determining
- locally randomized plan
- 11.7.1
- Logabex LX4 robot
- Computing
| Computing
- logic-based planning
- 2.4 to 2.5.3
- as satisfiability
- 2.5.3 to 2.5.3
- converting to state space
- 2.4.2 to 2.4.2
- in plan space
- 2.5.1 to 2.5.1
- operator
- 2.4.1
- via a planning graph
- 2.5.2 to Plan
- loop path
- The
- lost-cow problem
- Competitive
| Exercises
| Exercises
- low-discrepancy sampling
- 5.2.4 to Low-discrepancy
- low-dispersion sampling
- 5.2.3 to Dispersion
- lower envelope
- 6.5.2
| 6.5.2
| 6.5.2
| 6.5.2
| 6.5.2
| 9.3.3.2
- lower pairs
- 3.3.2
| 3.3.2
- lower value of a game
- 9.3.2
| 10.5.1.1
| Saddle
- Lozano-Pérez
- 4.
- Lozano-Pérez, Mason, and Taylor
- 12.5.1
- lunar lander
- 13.3.2.1 to 13.3.2.1
- Lyapunov function
- 8.5.1
| 15.1.2
| Determining to Lyapunov
- in planning
- Lyapunov to Lyapunov
- Lyapunov stability
- Equilibrium
| Equilibrium to Equilibrium
- uniform
- Equilibrium
- Lynch and Mason
- 13.1.3.1
| 13.1.3.1
- Möbius band
- 2D
| 2D
| The
| Exercises
| Exercises
- Mahalanobis metric
- The
- maneuver
- 14.2.3
- maneuver automaton
- 14.2.3
| 14.2.3
| 14.2.3
- Manhattan metric
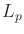
- Manhattan motion model
- General to General
- manifold
- 4.1.2
| Manifold
| Manifold to Higher
- embedding
- Manifold
- higher dimensional
- Higher to Higher
- one-dimensional
- 1D to 1D
- two-dimensional
- 2D to 2D
- with boundary
- Manifold
- manipulation graph
- Manipulation to Manipulation
- manipulation planning
- 7.3.2 to Multiple
- under uncertainty
- 12.5 to Squeezing
- manipulator
- The
| What
| Further
| 7.3.2 to Multiple
| 7.4
| 7.4
| 7.4
| Carton
| 13.4.2.1 to 13.4.2.1
| 14.6.3
| 14.6.3.3
- map building
- 12.3
| 12.3.1 to The
- marginalization
- Marginalization
| Marginalization to Random
| Probabilistic
| Probabilistic
| 11.2.3
| 11.2.3
| Discrete
- Markov chain
- 10.1.1
- Markov decision process
- 10.1.1
- Markov game
- Introducing
- Markov process
- 10.1.1
| 10.1.1
- mass matrix
- 13.4.1.2
- matching pennies
- 9.1.3 to 9.1.3
- Matlab
- 14.7
- matrix game
- 9.3.1
- matrix groups
- Matrix to Special
- matrix subgroup
- Matrix
- maximal ball
- Medial-axis
- maximum-clearance navigation function
- Maximum to Maximum
- maximum-clearance roadmap
- 6.2.3
| 6.2.3 to 6.2.3
- maze searching
- Algorithms to Algorithms
- Mealy/Moore machines
- 2.1.2
- means-end analysis
- Further
- measurable function
- 5.1.3
- measurable sets
- 5.1.3
- measure axioms
- 5.1.3
- measure space
- 5.1
- measure theory
- 5.1.3 to 5.1.4
| Defining to Defining
- measure zero
- 5.1.3
- mechanics
- 13.3 to 13.4.4
- Hamiltonian
- 13.4.4 to 13.4.4
- Lagrangian
- 13.4.1 to 13.4.3.2
- Newton-Euler
- 13.3 to A
- medial-axis sampling
- Medial-axis to Medial-axis
- Mersenne twister
- Pseudorandom
- metric space
- 5.1
| 5.1.1
| 5.1.1 to Cartesian
- Cartesian products of
- Cartesian to Cartesian
- definition
- 5.1.1
- for motion planning
- 5.1.2 to Pseudometrics
- from
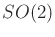
- 5.1.2
- from
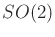
- to 5.1.2
- from
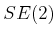
- 5.1.2
- from
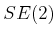
- to 5.1.2
- from
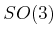
- 5.1.2
- from
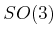
- to 5.1.2
- from
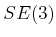
- 5.1.2
- from
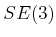
- to 5.1.2
- from
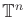
- 5.1.2 to 5.1.2
- nonpositively curved
- 14.7
- Riemannian manifold
- Riemannian to Riemannian
- robot displacement metric
- 5.1.2
- subspaces of
- Metric to Metric
- metric tensor
- Riemannian
- metrizable
- 5.1.1
- mine sweeping
- 7.6
- minimalism
- 12.5.2
- minimax
- 9.2.2
- minimum turning radius
- 13.1.2.1
- Minkowski difference
- 4.3.2
| 6.2.1
| 6.2.1
| Specialized
| Specialized
- Minkowski sum
- 4.3.2
- mod sensor
- 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- mode space
- 7.3
| 7.3.1
- mode transition function
- 7.3.1
- mode-dependent dynamics
- 7.3
- moment of a density
- Moment-based
- moment of force
- 13.3.2.2
- moment of inertia
- Simplifying
- moment of momentum
- 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.2
| The
| Differential
| The
- moment-based approximations
- Moment-based to Moment-based
- momentum
- 13.3.2.1
- monomial
- Polynomials
- monotone polygon
- Triangulation
- morphing a path
- Simply
- Morse function
- 8.4.4.3
- Morse theory
- 8.4.4.3
- motion capture
- Further
- motion command
- Motion
| Motion
| Motion to Motion
- motion planning
- 14.1.2.2
- motion primitive
- 14.2.3
| 14.2.3 to 14.2.3
| Designing to Designing
- multi-chained-form systems
- 15.5.2.3
- multi-level approach
- 14.6.2
- multi-linear interpolation
- 8.5.2.1
- multi-resolution grid
- Infinite
- multiobjective optimization
- 9.1.1.2 to 9.1.1.2
- multiple observations
- Receiving to Receiving
- multiple query
- Notions
| 5.6
- multiple shooting
- 14.7
- multiple-robot motion planning
- 7.2 to Planning
- multiple-robot optimality
- 7.7.2 to Computing
- multiply connected
- Simply
- Murphy's Law
- 9.2.2
- Murray and Sastry
- 15.5.2
- mutex condition
- Mutex
| Mutex to Mutex
- mutex relation
- Mutex
- NAG Fortran Library
- 14.7
- naive Bayes
- Receiving
- narrow-phase collision detection
- Two-phase
- NASA/Lockheed Martin X-33
- 14.1.3.1
| 14.1.3.1
| 14.1.3.1
- Nash equilibrium
- 9.4 to 9.4
| 9.4.1
| 9.4.1 to Summary
| 9.4.2
| 9.5.4 to 9.5.4
| 11.7
| 11.7.2
- admissible
- 9.4.1.1
- in a sequential game
- Nash to Nash
- nonuniqueness
- 9.4.1.1 to 9.4.1.1
- randomized
- 9.4.1.2
| 9.4.1.2 to 9.4.1.2
| 9.4.2
| 11.7.1
- nature
- 9.
| 9.2.1
- nature action space
- 9.2.1
- nature observation action
- Nature
| Nature
- nature sensing action
- 11.1.1
| 11.1.1
| 11.4.1
| Linear to Linear
| 11.5.3 to 11.5.3
- nature sensing actions
- 11.1.1
- navigation function
- 2.2.1
| 2.3.2
| Navigation to Other
- continuous space
- 8.4.1.2
- in the sense of Rimon-Koditschek
- 8.4.4.3 to 8.4.4.3
- stochastic
- 10.6.2
| 10.6.2
- navigation problem
- 12.3.1
| Algorithms to Algorithms
- negative literal
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
- neighborhood function
- 5.6.2
- neighborhood of a cover
- 8.5.1.1
- Neumann boundary condition
- 8.4.4.4
- Newton's laws
- Newton's to Newton's
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.2
| The
| The
| Inertia
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
- next-best-view problem
- 12.3.5
- NF2 (a navigation function)
- Maximum
- nicotine
- Designing
| Designing
- nilpotent
- 15.5.1
- nilpotent system
- 15.4.3.3
- nilpotentizable
- 15.5.1
- Nilsson
- Further
- Nixederreiter-Xing sequence
- Low-discrepancy
- nonconservative forces
- 13.4.3.2 to 13.4.3.2
- nonconvex
- polygon
- Nonconvex to Nonconvex
| Nonconvex
- polyhedron
- Nonconvex
- set
- Convex
- noncooperative game
- 9.
- noncritical regions
- Critical
- nondeterministic finite automaton
- 11.3.2
| 11.3.2 to 11.3.2
- nondeterministic information space
- 11.2.2 to 11.2.2
- approximations
- Conservative to Conservative
- examples
- 11.3.1 to 11.3.2
- planning on
- 12.1.2 to The
- nondeterministic Turing machine
- Languages
- nondeterministic uncertainty
- 9.2.2 to 9.2.2
- criticisms of
- 9.5.3 to 9.5.3
- nondirectional backprojections
- Backprojections
- nonholonomic
- 13.1.3.4
| Nonholonomic
| Nonholonomic
| 15.4
| 15.4.2.1
- nonholonomic constraints
- 13.1.2
- nonholonomic integrator
- 13.2.3
| 13.2.3 to 13.2.3
| 15.4.2.3
| 15.4.3.4
| 15.5.1
| The
| The
- showing it is nonholonomic
- 15.4.2.4 to 15.4.2.4
- steering
- 15.5.2.1 to 15.5.2.1
- nonholonomic metric
- The
- nonholonomic planning
- Parking
| Nonholonomic
| Nonholonomic to Nonholonomic
- nonholonomic system
- Underactuated to Underactuated
- nonholonomic system theory
- 15.4 to 15.4.3.5
- noninformative prior
- 9.5.2.2
| 9.5.2.2 to 9.5.2.2
- nonintegrable
- 15.4.2.1
- nonlinear optimization
- 14.7
- nonlinear programming
- 14.7
| 14.7 to 14.7
- nonlinear system
- 13.2.3 to 13.2.3
- affine in control
- 15.4.1 to 15.4.1
- affine-in-control
- 13.2.3
- nonparametric methods
- 9.5.2.3
- nonpositively curved space
- 14.7
- nonprehensile manipulation
- 12.5.2
| 12.5.2 to Squeezing
- nonrigid transformations
- 3.5
- nonzero-sum game
- 9.4 to 9.4.2
- with more than two players
- 9.4.2 to 9.4.2
- with two players
- 9.4.1 to Summary
- NP (complexity class)
- Languages
- null sensor
- 11.1.1
| 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- numerical continuation
- Stepping
- numerical integration
- Euler
- Euler to Euler
- multistep methods
- Multistep
| Multistep to Multistep
- Runge-Kutta
- Obtaining
| Runge-Kutta to Runge-Kutta
- single-step methods
- Multistep
- NURBS
- Nonuniform to Nonuniform
- OBB
- 5.3.2
| 5.3.2
- observability
- 13.2.2
- observation space
- Formulating
| 11.1.1
| 11.1.1
- observations
- 9.2.3 to Receiving
- obstacle region
- 3.2
| Obstacle
- in the C-space
- 4.3 to Chains
- 1D case
- to 4.3.2
| 4.3.2
- general case
- 4.3.3 to Chains
- polygonal case
- A to Computing
- polyhedral case
- A to A
- in the state space
- 14.1.3 to 14.1.3.2
- in the world
- 3.1
| 3.1 to Generalized
- polygonal case
- 6.2 to 6.2.4
- time-varying
- 7.1.1
| 7.1.3 to 7.1.3
- obstacles
- 3.1
- occupancy grid
- Bitmaps
| The
- Ochiai unknot benchmark
- Simplifying
| Simplifying
- octane transformations
- The to The
- odd/even sensor
- 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- odometric coordinates
- Solving
| Solving
| Algorithms
- odometry sensors
- Odometry to Odometry
- on-line algorithm
- 1.4.1
| Competitive to Competitive
- open ball
- Some
- open set
- 3.1.2
| 4.1.1
- open-loop
- control law
- Open-loop
- plan
- 8.1
- operator
- 2.4.1
- optical character recognition
- A to A
- optimal motion planning
- 7.7 to Computing
- optimal planning
- discrete
- 2.3
| 2.3.2 to 2.3.3
- fixed-length plans
- 2.3.1 to 2.3.1.2
- unspecified length
- 2.3.2 to 2.3.2
- optimization
- 9.1.1
| 9.1.1.1 to 9.1.1.2
- orientation sensor
- Simple
- oriented bounding box
- 5.3.2
| 5.3.2
- orienteering problem
- Further
- origami
- 7.5
- orthogonal group
- Matrix
- outdoor navigation
- General
- painting
- 7.6
- parallel manipulator
- 7.4
- parallel-jaw gripper
- Squeezing
- parameter estimation
- 9.2.4.2
| 9.2.4.2 to 9.2.4.2
- parameterization
- 1D
| Coordinates
- Pareto optimal
- 7.7.2
| 7.7.2
| 7.7.2 to Computing
| 9.1.1.2 to 9.1.1.2
| 9.4.1.1
| 9.4.1.1
| 9.4.2
| 9.5.2.1
- parking a car
- Parking
| 13.1.2.1
| 13.2.4.3
| 14.2.1.2
| Exercises
| Classical
| 15.4.2.3
- part configuration space
- Admissible
- partial grid
- Infinite
- partial plan
- 2.5.1
- particle
- 13.3.2
- dynamics
- 13.3.2 to 13.3.2.1
- falling
- 13.4.1.2 to 13.4.1.2
- on a sphere
- 13.4.3.1 to 13.4.3.1
- particle filtering
- Particle
| Particle to Particle
| Continuous
- path
- Paths
| Paths to Paths
- path connected
- Connected
- path tuning
- 7.1.3
| 7.1.3
- path-constrained phase space
- 14.6.3.3
- path-directed subdivision tree
- Other
- pattern classification
- 9.2.4.1
| 9.2.4.1 to A
- pebble
- Landmark
- peg-in-hole problem
- 12.5.1
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
- pendulum
- 13.3.2.1 to 13.3.2.1
- double
- Exercises
- Pennsylvania Turnpike
- 9.1.1.2
- perfect recall
- 11.7.1
- permissible action trajectories
- 14.1.1
- Pfaffian constraints
- 13.1.1.3 to 13.1.1.3
| 13.1.1.3
| 13.1.2.1
| 13.1.3.4
| 13.2.3
| 13.2.3
| 13.4.3.1
| 13.4.3.1
| 13.4.3.1
| 13.4.3.1
| 15.4.1
| 15.4.1
| 15.4.1
| 15.4.1
| 15.4.1
| 15.4.1
| 15.4.1
| 15.4.2.1
| 15.4.2.1
| 15.4.2.1
| 15.4.2.1
| 15.4.2.2
| 15.4.2.2
| 15.4.2.4
| 15.5.2.3
- pharmacophore
- Drug
- phase constraints
- 14.1.3.1
- phase space
- 13.2
| 13.2.1.1 to 13.2.4.3
- obstacles
- 14.1.3 to 14.1.3.2
- path-constrained
- 14.6.3.3 to 14.6.3.3
- phase transition equation
- 13.2.1.1
| 13.2.1.2
- phase vector
- 13.2.1.1
- Philip Hall basis
- 15.4.3.3
| 15.4.3.3
| 15.4.3.3 to 15.4.3.3
| 15.5.1 to 15.5.1
| Formal
| The
| Returning
| 15.5.2
- Piano Mover's Problem
- Definition to Definition
| 14.1.1
| 14.1.1
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.4
| 14.4.3
| 14.4.3
| Handling
| Distance
| 14.5.1
| 14.6.1
| 14.7
- piecewise-linear obstacle motion
- 7.1.1 to 7.1.1
| 7.1.3
- pitch rotation
- Yaw,
| Yaw,
- plan-and-transform method
- 14.6.2 to 14.6.2
- plan-based state transition graph
- Graph
- plan-space planning
- 2.5.1
| 2.5.1
- plane-sweep principle
- Plane-sweep to Algorithm
- radial sweep
- 6.2.4
| 8.4.3
- planetary navigation
- General
- planner
- 1.4.2 to 1.4.2
- planning graph
- 2.5.2
| Planning to Plan
- planning under sensing uncertainty
- 12. to Squeezing
- general methods
- 12.1 to The
- manipulation
- 12.5 to Squeezing
- Poinsot
- 13.3.3
| Completing
- point robot
- 6.2.1
- point-location problem
- 8.5.2.1
| Maintaining
- policy iteration
- 10.2.2
| 10.2.2 to 10.2.2
- for reinforcement learning
- Policy to Policy
- on an information space
- Policy to Policy
- with average cost-per-stage
- Solutions to Solutions
- with discounted cost
- Policy to Policy
- polygonal model
- 3.1.1 to Nonconvex
| 6.2 to 6.2.4
- face
- 6.2.1
- half-edge
- 6.2.1
- representation
- 6.2.1 to 6.2.1
- polyhedral model
- Polyhedral to Polyhedral
- polynomial
- Polynomials
| Polynomials to Polynomials
- coefficient
- Polynomials
- in formal Lie algebra
- Formal
- term
- Polynomials
- total degree
- Polynomials
- polynomial-time reducible
- Hardness
- POMDP
- 11.3.3
| 11.3.3 to 11.3.3
| 12.1.3 to The
- Pontryagin's minimum principle
- 10.2.2
| 14.7
| 15.2.3
| 15.2.3 to Time
| Pontryagin's
| Pontryagin's to Pontryagin's
- time-optimality case
- Time to Time
- portiernia
- 7.3.1
| 7.3.1 to 7.3.1
- position sensor
- Simple
- positive definite function
- Determining
- positive literal
- 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
- posterior
- Conditional
- potential energy
- 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.2
| 13.4.1.4
| 13.4.2
| 13.4.2.1
| 13.4.2.1
- potential function
- Pseudometrics
| 5.4.3
| 13.4.1.2
- attractive term
- 5.4.3
- continuous state space
- 8.4.1.2
- discrete
- Navigation
- repulsive term
- 5.4.3
- PQP (Proximity Query Package)
- Further
- predicate
- 2.4.1
- for geometric models
- Defining to Defining
- preimage of a function
- Continuous
- preimage of a motion command
- Preimages to Preimages
- preimage of an observation
- 11.1.1
- preimage planning
- 12.5.1
| 12.5.1 to Computing
- Princess and the Monster
- 11.7.2 to 11.7.2
- principle of virtual work
- 13.4.3.1
- principle subresultant coefficients
- The
- prior distribution
- Conditional
| 9.5.2.2 to 9.5.2.2
- prioritized planning
- Prioritized to Prioritized
- prismatic joint
- Attaching
| Attaching
| Attaching
| Homogeneous
| The
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- 9.4.1.1 to 9.4.1.1
| 9.5.4
| 9.5.4
- probabilistic completeness
- Notions
- probabilistic information space
- 11.2.3 to Sensor
- approximations
- Moment-based to Moment-based
- examples
- 11.3.3 to 11.3.3
- planning on
- 12.1.3 to The
- probabilistic information state
- computation of
- 11.6 to Particle
- probabilistic uncertainty
- 9.2.2 to 9.2.2
- criticisms of
- 9.5.2 to 9.5.2.3
- probability function
- Probability
- probability measure
- 5.1.3 to 5.1.3
- probability space
- Probability to Probability
- probability theory
- 9.1.2 to Expectation
- problem solving
- 2.
| 2.
- product of inertia
- Simplifying
- projection sensors
- Simple to Simple
| 11.5.2 to 11.5.2
- projective geometry
- Combining
- projective space
- Higher
- protein cavity
- 8.1
- protein folding
- Designing
| Protein to Protein
- proximity sensor
- Boundary
- pseudometric
- Pseudometrics to Pseudometrics
| Sampling-based
| Sampling-based
- pseudorandom number generation
- Pseudorandom to Pseudorandom
- linear congruential
- Pseudorandom
- PSPACE
- Languages
- Puma 560 robot
- The
- pure strategy
- 9.1.3
- pursuit-evasion game
- 11.7.2
| 13.5.2
| 13.5.2
- pushing a box
- 13.1.3.1 to 13.1.3.1
- Q-factor
- 10.4.3
- Q-learning
- 10.4.3 to Policy
- quadratic cost functional
- 15.2.2
- quadratic potential function
- 8.4.1.2 to 8.4.1.2
- quantified variables
- Tarski
- quantifier
- Tarski
- quantifier-elimination problem
- Tarski
| The
- quantifier-free formula
- Tarski
- quasi-static
- 13.1.3
- quaternion
- Quaternions to Finding
- from a rotation matrix
- Finding to Finding
- quotient topology
- Identifications
- radar map
- Radar
| Radar to Radar
- radial sweep
- 6.2.4
| 8.4.3
- random loop generator
- 7.4.2
| Loop
| Loop to Loop
- random sampling
- 5.2.2 to Testing
- of
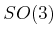
- Generating
- of
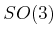
- to Generating
- of directions
- Generating to Generating
- tests
- Testing to Testing
- random variable
- Random
| Random to Expectation
- random-walk planner
- Random-walk to Random-walk
- randomized algorithm
- General
- randomized lower value
- 9.3.3.1
| 10.5.1.2
| Value
- randomized plan
- 10.5.1
| 10.5.1
| Defining
- randomized potential field
- 5.4.3
| 5.4.3 to 5.4.3
| 8.4.1.2
- under differential constraints
- Randomized to Randomized
- randomized saddle point
- 9.3.3.1
- randomized security plan
- 10.5.1.2
- randomized strategy
- 9.1.3
| 9.1.3 to 9.1.3
- randomized upper value
- 9.3.3.1
- randomized value
- 9.3.3.1
| 10.5.1.2
- range scanner
- Depth-mapping
- range space (for discrepancy)
- 5.2.4
- rapidly exploring dense tree
- 5.5
| 5.5
| 5.5 to More
| Sampling-based
| Fixed-path
| Sampling-based
| Computing
| Computing
- exploration
- 5.5 to 5.5.1
- finding nearest points
- 5.5.2 to Approximate
- making planners
- 5.5.3 to More
- under differential constraints
- 14.4.3 to Designing
- Rapoport
- 9.5.4
- rational decision maker
- 9.3.1
| 9.5.1.1
| 9.5.1.2
- reachability graph
- 14.2.2.1
| 14.2.2.1 to 14.2.2.1
- reachability tree
- 14.2.2.1
| 14.2.2.1 to 14.2.2.1
- reachable set
- 14.2.1
| 14.2.1.1 to 14.2.1.3
- backward
- Domains
- for simple car models
- 14.2.1.2 to 14.2.1.2
- real algebraic numbers
- Real
| Real to Real
- reality television
- 9.5.1.1 to 9.5.1.1
- reckless driving
- ``Wreckless''
- recognizability
- 11.3.1
| Backprojections
- reconfigurable robot
- 7.3.1
- recontamination
- 12.4.2
- Reeds-Shepp car
- 13.1.2.1
| Symmetric
| 14.2.1.2
| 14.2.1.2
| 14.2.1.2
| 14.6.2
- Reeds-Shepp curves
- 15.3.2
| 15.3.2 to 15.3.2
- refinement of a plan
- Refinement
| 14.6.1
- reflex vertex
- 6.2.4
- region of inevitable collision
- 14.1.3.2
| 14.1.3.2
| 14.1.3.2 to 14.1.3.2
- regret
- Regret
| Regret to Regret
| Regret to Regret
- regret matrix
- Regret
| Regret
- reinforcement learning
- 10.4
| 10.4.1
| Terminology to Policy
- evaluating a plan
- 10.4.2 to Temporal
- general framework
- The to The
- terminology
- Terminology to Terminology
- relative value iteration
- Solutions
- repulsive vertex
- 8.4.2
- reroute path
- Solving
- resolution
- 5.2.3
- resolution completeness
- Notions
| 5.2.3
| 5.2.3
| Grid
| Fixed-roadmap
| 14.2.2.2
| Resolution to Resolution
| Ensuring to Ensuring
- under differential constraints
- 14.2.2.2 to 14.2.2.3
- resultant
- force
- 13.3.3
- moment
- 13.3.3
- reverse-time system simulation
- Reverse-time to Reverse-time
- revolute joint
- Attaching
| Attaching
| Attaching
| Attaching
| Attaching
| Homogeneous
| Homogeneous
| 3.3.2
| 3.3.2
| 3.3.2
| 3.3.2
| The
| The
| The
| The
| 8.1
| Common
| Flexible
| Exercises
- reward
- Terminology
- reward function
- 9.1.1.1
- reward functional
- Terminology
- reward space
- 9.5.1.1
- Riemannian manifold
- 13.4.1.2
- Riemannian metric
- Riemannian
| Riemannian to Riemannian
- Riemannian tensor
- Riemannian
- Rimon
- Navigation
| 8.4.4.3
- risk
- conditional Bayes'
- Optimal
- frequentist
- 9.5.2.1
- roadmap
- directed
- Sampling-based
- general requirements
- Roadmaps to Roadmaps
- robot displacement metric
- 5.1.2 to 5.1.2
- robot-robot collisions
- 7.2.1
- Rock-Paper-Scissors
- 9.5.4
| Exercises
- roll rotation
- Yaw,
| Yaw,
- rolling a ball
- 13.1.3.3 to 13.1.3.3
- rotation
- 2D
- Rotation to Combining
- 3D with quaternions
- Quaternions to Quaternions
- 3D with yaw-pitch-roll
- Yaw, to The
- Rubik's cube
- 1.1
| Discrete
| Discrete
| Time
| 2.1.2
- Runge-Kutta
- Obtaining
- Russell and Norvig
- 2.
- sample point of a cell
- Defining
- sample sequence
- 5.2.1
- sample set
- 5.2.1
- sample space (of a probability space)
- Probability
- sampling-based neighborhood graph
- 8.5.1.3
- sampling-based planning
- for closed chains
- Sampling-based to Computing
- philosophy
- 5.
| 5.
| 5. to 5.
- time-varying
- Sampling-based to Sampling-based
- under differential constraints
- 14.3 to Sampling-based
- with feedback
- 8.5 to 8.5.2.3
| 14.5 to 14.5.2
- sampling-based roadmap
 -goodness
-goodness
- Some
- analysis
- Some to Some
- basic method
- 5.6 to Some
- boundary sampling
- Sampling to Sampling
- bridge-test sampling
- Bridge-test to Bridge-test
- Guassian sampling
- Gaussian to Gaussian
- medial-axis sampling
- Medial-axis to Medial-axis
- preprocessing phase
- Generic to Selecting
- query phase
- Query to Query
- vertex enhancement
- Vertex to Vertex
- visibility roadmap
- 5.6.2 to 5.6.2
- sampling-based roadmaps
- 5.6
| 5.6 to Medial-axis
- under differential constraints
- Sampling-based to Sampling-based
- Sard's Theorem
- 8.4.4.3
- scalarization
- Scalarization to Scalarization
- scaling an object
- Linear
- screw transformation
- Two
- sealing cracks
- Sealing
- search algorithms
- 7.1.3
- adaptation to continuous spaces
- 5.4.2 to Grid
- under differential constraints
- 14.3.4 to 14.3.4
| Searching to Searching
- unified view
- 2.2.4 to 2.2.4
- search graph
- 2.2.4
| 5.4.1
| 14.3.4
- searching an environment
- 12.3.1
- second-order controllable systems
- 15.5.2.2
- second-order differential drive
- 13.2.4.3
- second-order unicycle
- 13.2.4.1
- section (of a cylinder)
- The
- sector (of a cylinder)
- The
- security plan
- 10.5.1.1
| 10.5.1.1 to 10.5.1.1
| Value
- security strategy
- 9.3.2
- randomized
- 9.3.3.1
- selective sensor
- 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- semi-algebraic decomposition
- Semi-algebraic
- semi-algebraic model
- 3.1.2 to 3.1.2
- semi-algebraic set
- 3.1.2
- sensing history
- History
- sensor feedback
- Sensor
- sensor mapping
- 11.1.1
| 11.1.1
| 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
| 11.4.2 to 11.4.2
- sensor observation
- 11.
- sensorless manipulation
- 12.5.2
- sensorless planning
- 11.3.1
| 11.3.1 to 11.3.1
| 11.5.4 to 11.5.4
- sensors
- continuous
- 11.5.1 to Odometry
- discrete
- 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- sequential game
- 10.5
| 10.5.1 to Introducing
- information space of
- 11.7.1 to 11.7.2
- Markov assumption
- 10.1.1 to 10.1.1
- more than two players
- Introducing to Introducing
- on state spaces
- 10.5.2 to Introducing
- saddle point
- 10.5.1.2 to 10.5.1.3
| Saddle to Saddle
| 11.7
| 11.7.1 to 11.7.1
| 11.7.1 to 11.7.1
| 11.7.2 to 11.7.2
- zero-sum with nature
- Introducing to Introducing
- shadow component
- 12.3.4
- shadow region
- 12.3.4
- shearing transformation
- Linear
- shooting methods
- 14.7
- shortest-path functional
- 13.4.1.1 to 13.4.1.1
- shortest-path roadmap
- 6.2.4
| 6.2.4
| 6.2.4 to 6.2.4
| Using
- SICK LMS-200
- Depth-mapping
- sigma algebra
- 5.1.3
- sign assignment
- Semi-algebraic
- sign sensor
- 11.1.1 to 11.1.1
- sign-invariant region
- Semi-algebraic
- silhouette curves
- 6.4.3
| 6.4.3
- simple polygon
- Nonconvex
- simple-car model
- 13.1.2.1 to 13.1.2.1
- two-car game
- 13.5.2 to 13.5.2
- with nature
- 13.5.1 to 13.5.1
- simple-unicycle model
- 13.1.2.3 to 13.1.2.3
- simplicial complex
- 6.3.1
| Simplicial
| Simplicial
| Simplicial to Simplicial
| Singular
| Singular to Singular
- simply connected space
- Simply
- Simpson paradox
- 9.5.1.2
- simulation-based methods
- Terminology
- simultaneous localization and mapping
- 12.3.1
- single query
- Notions
| 5.4.1
- single shooting
- 14.7
- singular 0-simplex
- Singular
- singular arcs
- 15.2.3
- singular complex
- 6.3.1
| Singular
| Singular
| Singular
- singular distribution
- 15.4.2.2
- singular matrix
- 6.4.3
- singular point of a distribution
- 15.4.2.2
- singular simplex
- Singular
- singular value decomposition (SVD)
- 10.2.2
- situation calculus
- 2.5.3
- skew symmetry
- 15.4.3.1
| 15.4.3.3
- SLAM
- 12.3
| 12.3.1 to The
- probabilistic
- 12.3.5 to The
- sliding-mode control
- Piecewise-smooth
- sliding-tile puzzle
- 1.1
| Discrete
| Discrete
| 2.1.2
- small-time local controllability
- 13.1.2
| 13.1.2.1
| 14.6.2
| STLC: to STLC:
| 15.3.1
| 15.3.2
| 15.4
| 15.4.2
| 15.4.3
| 15.4.3.4 to 15.4.3.5
| 15.5
| 15.5.1
| Decoupling
- smooth differential drive
- 13.2.4.3 to 13.2.4.3
- smooth distribution
- 15.4.2.2
- smooth function
- Smoothness
- smooth manifold
- Manifold
| 8.3.2
| Coordinates to Vector
| 15.4.2.2
-
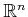
- Coordinates
-
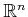
- to Coordinates
-
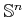
- Coordinates
-
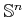
- to Coordinates
-
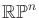
- Coordinates
-
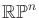
- to Coordinates
- Riemannian
- Riemannian to Riemannian
- smooth structure
- Coordinates
- smoothness of a function
- Smoothness to Smoothness
- Sobol sequence
- Low-discrepancy
- Sod's Law
- 9.2.2
- Sokoban
- Lower
- solid representation
- 3.1
- solution in the sense of Filipov
- Piecewise-smooth
- solution trajectory
- An
| Vector
- span of vector fields
- 15.4.2.2
- spanning tree
- Spanning
- spanning-tree covering
- Spanning to Spanning
- spatial constraints
- Drug
- special Euclidean group
- Special
| Special to Special
| Special to Special
- special orthogonal group
- Matrix
- speedometer
- Simple
- spherical coordinates
- Tangent
- spherical joint
- The
| 8.1
- spherical linear interpolation
- 5.1.2
- spine curve
- Generalized
- spiral search
- Competitive
- squeeze function
- Squeezing
- squeezing parts
- Squeezing to Squeezing
- stability of a system
- 15.1.1 to Determining
- time-varying case
- Time-varying to Time-varying
- uniform
- Equilibrium
- stable configuration space
- Stable
- stage-dependent plan
- Defining
- standard grid
- Making
- star algorithm
- A to A
- star-shaped regions
- 8.4.4.3
- state estimation
- Making to Making
- state history
- 8.4.1.1
- state mapping
- 11.4.1
- state space
- 2.1.1
| 2.1.1
- state trajectory
- 8.2.1
| 8.4.1.1
| 14.1.1
- state transition equation
- 2.1.1
| 2.1.1
| 13.2.1.1
| 13.2.1.2
- state transition function
- 2.1.1
| 2.1.1
- state transition graph
- 2.1.1
- state transition matrix
- Probabilistic
- state-nature mapping
- 11.4.1
| 11.4.2
- state-sensor mapping
- 11.4.2
- state-space discretization
- 14.4.2 to Backward
- stationary cost-to-go function
- 2.3.2
| Convergence
| Convergence
| Using
- stationary differential equations
- Vector
- statistical decision theory
- 9.2.4
- steering methods
- 14.3.3
| 15.5 to Dynamic
- piecewise-constant actions
- 15.5.1 to Using
- sinusoidal action trajectories
- 15.5.2 to 15.5.2.3
- steering problem
- 14.1.2.2
- Stentz's algorithm
- General
| 12.3.2 to Interpretation
- stereographic projection
- Solving
| Coordinates
- sticking
- Compliant
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Computing
| Computing
- stochastic control theory
- 10.
- stochastic differential equation
- 13.5.1
- stochastic fractal
- 5.5.1
- stochastic iterative algorithm
- Temporal
| Temporal
- stochastic shortest-path problem
- Further
- strange topology
- Some
- strategy
- Formulating
- STRIPS
- 2.
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.1
| 2.4.2 to 2.4.2
| 2.5
- strong backprojection
- Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
- structure problem
- Protein
- sub-Riemannian metric
- The
- subgroup
- Matrix
- subjective probabilities
- 9.5.2.2
- subspace topology
- Some
| Some to Some
- sufficient information mapping
- Constructing
- sufficient statistic
- Constructing
- Sukharev grid
- Making
- superquadric
- Superquadrics
- supremum
- Dispersion
| 9.1.1.1
- Sussmann and Tang
- 15.3.2
| 15.3.2
- swath
- 5.5.1
| 5.5.1
| 5.5.1
| 14.2.2.1
| 14.2.2.1
| 14.2.2.1
| 14.2.3
| 14.3.4
- swath-point selection method
- 5.5.1
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
- Swiss cheese
- Simply
- switching boundary
- Piecewise-smooth
- switching time
- 15.2.3
- symmetric systems
- Symmetric to Symmetric
- symmetric Turing machine
- Lower
- symmetry class
- Solving
- symplectic manifold
- 13.4.4
- system
- 13.
| Open-loop
- determining whether controllable
- 15.4.3 to 15.4.3.5
- determining whether nonholonomic
- 15.4.2 to 15.4.2.4
- distribution
- 15.4.2.2
- simulator
- 14.3.2 to Reverse-time
- system vector fields
- 15.4.1
- systematic search
- 2.2 to 2.2
- tangent bundle
- Vector
| 13.2.1.2
| 15.4.2.2
- tangent point
- 14.6.3.5
- tangent space
- Vector
| Vector to Vector
| 8.3.2
| 8.3.2
| 8.3.2 to 8.3.2
| Tangent
- on a manifold
- Tangent to Tangent
- TangentBug
- Using
- Tarski sentence
- Tarski
- Tarski-Seidenberg Theorem
- Semi-algebraic
- Taylor series
- 15.2.1.2
| 15.2.1.3
| 15.4.2.3
| 15.4.2.3
| 15.4.2.3
| 15.4.2.3
- team theory
- 11.7.2
- temporal difference
- Temporal
| Temporal to Temporal
- temporal logic
- Further
- termination action
- 2.3.2
| 11.1.3
- THC
- Designing
| Designing
- theory of computation
- 6.5.1
- time scaling
- 7.1.3
| Trajectory
- time-invariant
- 13.2.2
- time-limited reachable set
- 14.2.1.2
- time-monotonic path
- 7.1.1
| Sampling-based
| Combinatorial
| Combinatorial
| Combinatorial
| Combinatorial
| 7.1.3
| 7.1.3
- time-optimal trajectory planning
- 14.6.3.5 to 14.6.3.5
- time-varying motion planning
- 7.1 to 7.1.3
- algebraic obstacle motion
- Combinatorial
- bounded speed
- Bounded to Bounded
- unbounded speed
- 7.1.1 to Combinatorial
- timing function
- 7.1.3
- tire skidding
- A
- Tit-for-Tat
- 9.5.4
- topological complexity
- Further
- topological graph
- Homeomorphism:
| Homeomorphism: to Homeomorphism:
| 14.2.2.1
- topological property
- 14.6.2
| 15.4.3.4
- topological space
- 4.1.1
| 4.1.1 to Homeomorphism:
- connected
- Connected
| Connected
- identification
- Identifications to Identifications
- metrizable
- 5.1.1
- path connected
- Connected
- simply connected
- Simply
| Simply
- topologist's sine curve
- Connected
- torque
- 13.3.2.1
| 13.3.2.2
| 13.4.2.1
- torus
- 2D
| Higher
| The
| 4.4.2
| Two
| A
| Three
- total differential
- 13.4.4
| 13.4.4
| 13.4.4
| 13.4.4
- tower exponentiation
- 6.5.2
- Towers of Hanoi
- Exercises
- trailers
- 13.1.2.4 to 13.1.2.4
- trajectory
- An
- trajectory optimization
- 14.7
| 14.7 to 14.7
- trajectory planning
- Trajectory
| Trajectory to Trajectory
- path-constrained
- 14.6.3 to 14.6.3.5
- transcription
- 14.7
- transfer mode
- Stable
- transfer path
- Stable
- transformations
- 2D chain
- 3.3.1 to Homogeneous
- 2D rigid body
- 3.2.2 to Combining
- 3D chain
- 3.3.2 to The
- 3D rigid body
- 3.2.3 to The
- general concepts
- 3.2.1 to Defining
- kinematic tree
- 3.4 to What
- nonrigid
- 3.5 to Flexible
- transit path
- Stable
- transition configurations (mode change)
- Stable
- translating a disc
- Translation
- trapped on a surface
- 13.1.3.4 to 13.1.3.4
- Traveling Salesman Problem
- 7.6
- tray tilting
- 11.5.4 to 11.5.4
| 12.5.2
- triangle fan
- 3D
- triangle inequality
- 5.1.1
- triangle model
- 3D to 3D
- triangle strip
- 3D
- triangular enumeration
- 14.2.2.3
- triangulation
- Warning:
| Simplicial
| Triangulation
| Triangulation to Triangulation
| Further
| 8.4.2
- tricycle
- 13.1.2.1
- trim trajectory
- 14.2.3
- trivial operator
- Layer-by-layer
- trivial topology
- Some
- Turing machine
- 1.4.1
| 6.5.1
- two-point boundary value problem
- 14.1.1
| 14.1.2.2
| 14.2.1
| 14.2.2.1
| 14.3
| Reverse-time
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.3
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| 14.3.4
| 14.4.1.1
| Searching
| Backward
| Backward
| 14.4.3
| Tree-based
| Tree-based
| Tree-based
| Tree-based
| Sampling-based
| 14.7
| 14.7
| 14.7
| 14.7
| 15.
| 15.
| Classical
| 15.5
- Type EE contact
- A
| 3D
- Type EV contact
- Computing
| Computing
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| Exercises
- Type FV contact
- A
| 3D
- Type VE contact
- Computing
| Computing
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| 4.3.3
| Exercises
| Exercises
- Type VF contact
- A
| 3D
- Udupa
- 4.
- uncertainty
- brief overview
- Overview to Uncertainty
- due to partial predictability
- Planning
| 10.1 to Policy
- due to sensing
- Planning
| 11. to 11.7.2
| 12. to Squeezing
- underactuated system
- 13.1.2
| Underactuation
| 14.2.2.1
| Underactuated to Underactuated
- unicycle
- 13.1.2.3 to 13.1.2.3
| 13.2.4.1 to 13.2.4.3
- uniform random
- 5.2.2
- union-find algorithm
- Grid
| Generic
- unique point
- Algorithms
- unit complex number
- Using
- unit quaternions
- Quaternions
- unknot
- Simplifying
- unsupervised classification
- 9.2.4.1
- unvisited states
- 2.2.1
- upper envelope
- 9.3.3.2
- upper value of a game
- 9.3.2
| 10.5.1.1
| Saddle
- utility function
- 9.5.1.3 to 9.5.1.3
- utility of money
- 9.5.1.3 to 9.5.1.3
- utility theory
- 9.5.1
| 9.5.1.1 to 9.5.1.3
- vacuum cleaning
- 7.6
- value iteration
- 2.3.1
| 2.3.1
- backward
- 2.3.1.1 to 2.3.1.1
- convergence issues
- Convergence to Convergence
- forward
- 2.3.1.2 to 2.3.1.2
- relative
- Solutions
- with interpolation
- 8.5.2 to Continuous
- van der Corput sequence
- The to The
| Infinite
| Infinite
| Dispersion
| Low-discrepancy
| Low-discrepancy
| 5.3.4
| 5.3.4
| Generic
- variation of a function
- 13.4.1.1
- variety
- 4.4
| Varieties
| Varieties to Varieties
- for 2D chains
- 4.4.2 to Three
- for general linkages
- 4.4.3 to 4.4.3
- vector field
- 8.3.1
| Vector to Piecewise-smooth
| Vector
| Vector to Vector
| 13.1.1.2
- equilibrium point
- Equilibrium
- normalized
- 8.4.1.1
- over a cell complex
- 8.4.2 to 8.4.2
- piecewise-smooth
- Piecewise-smooth to Piecewise-smooth
- vector space
- Vector
| Vector
| Vector to Vector
-
 over
over
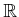
- Vector
-
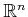 over
over
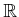
- to Vector
- of functions
- Vector to Vector
- velocity field
- Vector
| Vector to Vector
- velocity-tuning method
- 7.1.3 to 7.1.3
- vertex selection method
- 5.4.1
| 5.4.1
| 5.4.1
| 5.4.1
| 5.4.3
| Ariadne's
| Expansive-space
| Expansive-space
| Random-walk
| 5.5.1
| 5.5.1
- vertical decomposition
- 6.2.2 to Algorithm
| Singular to Singular
| 7.1.3
| 7.1.3
- 3D
- 6.3.3 to 6.3.3
- violation-free state
- 14.1.3.1
- virtual human
- Virtual
- VisBug
- Using
- visibility polygon
- 12.2.2
- visibility region
- 12.3.4
- visibility roadmap
- 5.6.2
- visibility sensor
- Depth-mapping
| 12.2.2
- visibility skeleton
- 12.2.2
- visibility-based pursuit-evasion
- 12.4
| 12.4.1 to 12.4.3
- a sequence of hard problems
- 12.4.1
- complete algorithm
- 12.4.2 to 12.4.2
- problem formulation
- 12.4.1 to 12.4.1
- variations
- 12.4.3 to 12.4.3
- Voronoi diagram
- Testing
- Voronoi region
- Testing
| Low-discrepancy
| Low-discrepancy
| 5.3.3
| 5.3.3
| 5.3.3
| 5.3.3
| 5.3.3
| A
- Voronoi vertex
- Dispersion
- wall clock
- Odometry
- wall following
- Algorithms
- warping a path
- Simply
- wavefront
- Euclidean
- wavefront propagation
- Wavefront to Wavefront
| 8.5.2.3
- wavelet
- Euclidean
- way point
- 8.4.3
- weak backprojection
- Backprojections
| Backprojections
| 10.6.1
| Backprojections
| Backprojections
- weighted-region problem
- General to General
- Weiner process
- 13.5.1
- Whitney's embedding theorem
- Manifold
| Identifications
- with probability one
- A
- word (sequence of motion primitives)
- 15.3.1
- world
- 3.1
| 13.3.1
- world frame
- Defining
- worst-case analysis
- 9.2.2
| The
| The
- wrench (from mechanics)
- 13.3.3
- yaw rotation
- Yaw,
| Yaw,
- zero-sum game
- 9.3
| 9.3 to 9.3.3.2
- matrix representation of
- 9.3.1 to 9.3.1
- randomized saddle point
- 9.3.3.1 to 9.3.3.2
- randomized value of
- 9.3.3.1
- regret in
- Regret to Regret
- saddle point
- Saddle
| Saddle to Saddle
- value of
- Saddle
Steven M LaValle
2020-08-14
