Often times, it is useful to talk about frequency instead of wavelength. The frequency is the number of times per second that wave peaks pass through a fixed location. Using both the wavelength 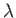 and the speed
and the speed 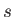 , the frequency
, the frequency 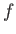 is calculated as:
is calculated as:
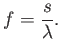 |
(4.1) |
The speed of light in a vacuum is a universal constant 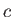 with value approximately equal to
with value approximately equal to
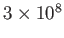 m/s. In this case,
m/s. In this case, 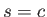 in (4.1). Light propagates roughly
in (4.1). Light propagates roughly 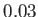 percent faster in a vacuum than in air, causing the difference to be neglected in most engineering calculations. Visible light in air has a frequency range of roughly 400 to 800 terahertz, which is obtained by applying (4.1). As light propagates through denser media, such as water or lenses,
percent faster in a vacuum than in air, causing the difference to be neglected in most engineering calculations. Visible light in air has a frequency range of roughly 400 to 800 terahertz, which is obtained by applying (4.1). As light propagates through denser media, such as water or lenses, 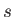 is significantly smaller; that difference is the basis of optical systems, which are covered next.
is significantly smaller; that difference is the basis of optical systems, which are covered next.
Steven M LaValle
2020-11-11

![]() and the speed
and the speed ![]() , the frequency
, the frequency ![]() is calculated as:
is calculated as: